Data-Centric Software Architecture helps to increase the maintainability, reusability, and scalability of a system. There are 2 types of components:
- Central Data – the component used to store and serve data across all components that connect to it.
- Data Accessors – the components that connect to the central data component. The data accessors make queries and transactions against the information stored in the database.
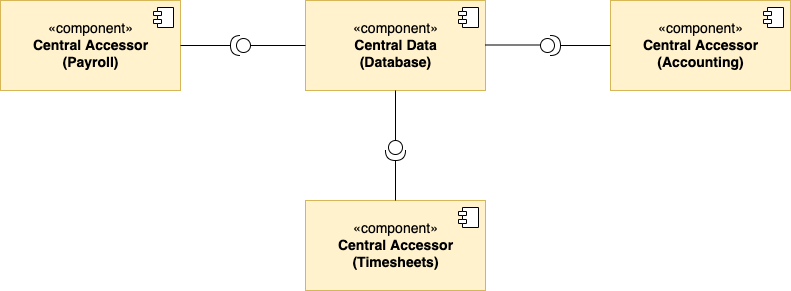
The data accessors are separated from one another and communicate only to the central data component. The central data facilitates data sharing by saving the desired information from the current state of the system and serving data as requested.
Two main properties of a database:
- Data Integrity – a database will ensure the data is accurate and consistent over its lifespan.
- Data Persistence – a database will make sure that data will continue to live on after a process has been terminated.
In a data-centric architectural design, the central data is passive. The database is generally not involved in heavy data processing or large amounts of business logic. The central data is primarily concerned with storing and serving the information.
A data accessor is essentially any component that connects to the database, which is characterized by its abilities to:
- Share a set of data while being able to operate independently.
- Communicate with the database through database queries and transactions that accessors do not need to interact directly with each other and therefore, do not need to know about each other.
- Query the database to obtain shared system information. This is used to get data in order to perform computations. And save the new state of the system back into the database using transactions. Data is stored back into the database once the data accessor has finished its processing.
- A data accessor contains all the business rules required to perform its functions. This means that this software architecture enables you to separate concerns into different specialized data accessors.
- Data accessors can be controlled. So, an end-user only has permission for the ones they need on a day-to-day basis.
Having functionally independent data accessors also means that your system can easily be scaled up. You can easily build and integrate additional functions without having to worry about affecting the others.
Disadvantages:
- The system becomes heavily reliant on the central data component. If the data server goes off line, becomes unusable or contains corrupted data, your entire system will be affected.
- It is difficult to change the existing data schema. Database changes can be hard to implement, especially if there’s a massive amount of data stored. Data schema changes will also affect your data accessors.