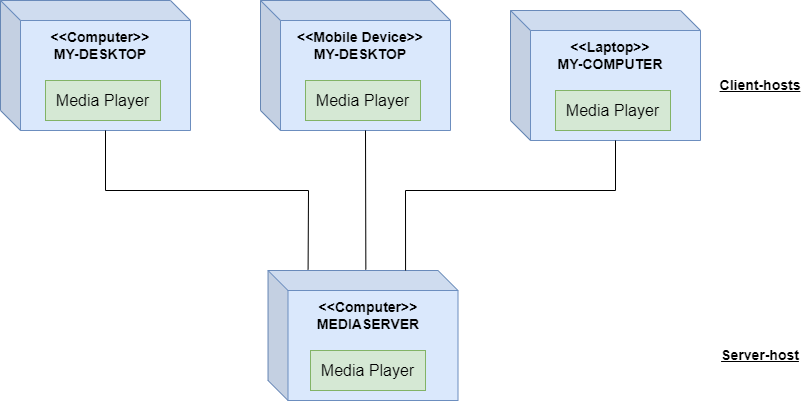
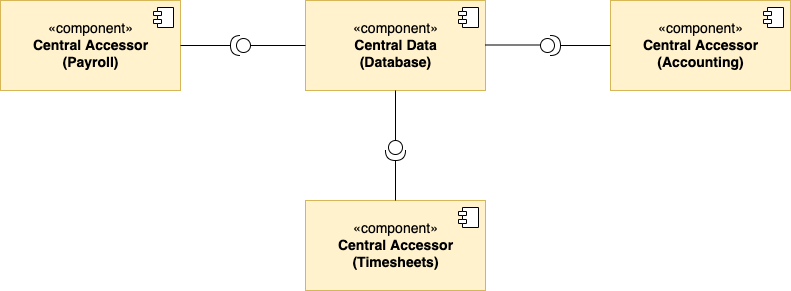
Another name of the n-Tier is Multitier. Tiers often refer to components that are on different physical machines. The number of tiers varies quite a bit, 3- and 4-tier architectures are quite common, but any number is possible. So this architecture is called n-Tier or a Multitier.
The relationship between 2-Tiers in an n-Tier architecture is often a client/server relationship. The server side provides services. This could be storing information in a database, performing computation tasks, any sort of service. The client-side requests these services through messages. The communication between the two sides is called Request-Response. A tier can act as both a server and a client, simultaneously fulfilling the requests of its clients and making requests of its servers.
2-Tier Architecture (Client Tier and Data Tier):